Regenerative Medicine
Understanding Regenerative Medicine
At The Renue Regenerative Medical Centre, we practice Regenerative Medicine, a pioneering branch of medicine that studies methods to regrow, repair, or replace malfunctioning or damaged cells, organs, and tissues. Regenerative medicine includes complex processes such as collecting and producing Stem Cells, and body tissue engineering.
Stem Cells: What are they?
The human body is an exquisite machine that can flawlessly execute diverse functions for us to live. Many types of cells perform specialized functions: brain cells, bone cells, skin cells, blood cells, and more. Groups of specialized cells form tissues that form organs—for example, the liver, lungs, and heart—each with a particular job within the body.
But how are such specialized cells formed? We know that human reproduction starts with a single cell: the fertilized egg or zygote. The zygote divides itself, originating other cells that later go through a transformation process called differentiation. Differentiation is the process that allows the new cells to specialize and perform a specific function in the body.
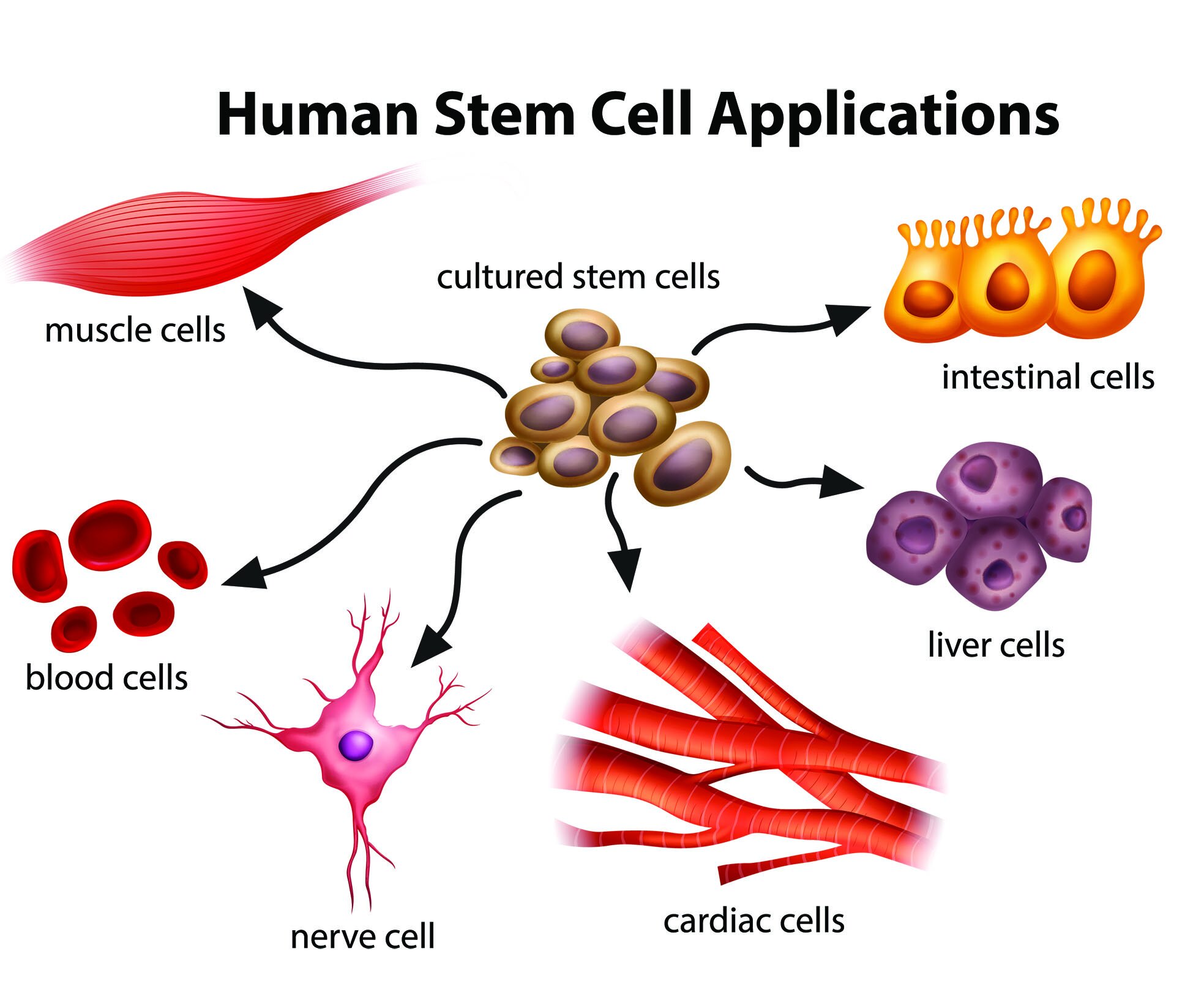
The new cells that haven’t differentiated into specialized ones are called Stem Cells; they have the ability to divide and generate copies of themselves or differentiate into specialized cells an unlimited number of times. Other body cells can only replicate a few times before they die.
Stem Cells can be classified according to their origin:
Adult Stem Cells: present in adult individuals to replace sick cells or repair damaged tissue.
Embryonic Stem Cells: found in embryos, they develop into all the fetus’s tissues.
Perinatal Stem Cells: present in tissues discarded after a baby’s birth (placenta, umbilical cord, and amniotic membrane and fluid)
Stem Cells: Why are they important?
Stem cells can replicate into other stem cells or differentiate and become specialized cells that form tissues and organs. This ability is what makes them unique. Most body cells are specialized (differentiated) and execute only one function in a specific organ or tissue. Stem Cells’ primary purpose is to replace damaged or missing specialized cells; they can be called the body’s cell generator and have the following characteristics or functions:
Indefinite replication or self-renewal
Present in several body tissues: fatty tissue, umbilical cord cells and blood, bone marrow, dental pulp, and others
Ability to migrate to specific areas of the body
Replace damaged or sick cells
Repair damaged body tissue
Generate specialized cells
Stimulate or activate other cells
Because of such unique characteristics, SCs play an essential role in the body's healing process, which is the object of regenerative medicine. With the discovery and isolation of Stem Cells, researchers have developed regeneration therapies that introduce stem cells into damaged tissues to treat diseases or injuries, increasing the chances of reducing suffering and loss of function in individuals. Other stem cell applications are body tissue engineering, artificial organ production, and even drug testing.
Stem Cell Therapy at Renue
Stem Cell Therapy (SCT) is the most innovative and advanced treatment option for treating tissue damage due to illness or injury. A concentrated product of human stem cells is processed, purified, and then applied to the patient’s affected tissues according to their needs.
The main objective of SCT is to provide patients with a satisfactory treatment that can stimulate their immunity and promote tissue regeneration in affected areas. Moreover, it helps improve symptoms of chronic illness without the adverse effects and risks of the other treatment options. Thus, SCT is a highly effective and viable option for patients when their current intervention or other treatments do not improve their symptoms.
At Renue, the initial patient’s evaluation comprises medical information reviews, laboratory work or tests, diagnostic imaging, and other procedures – see the Renue Journey. These patient evaluation techniques help determine the stage or severity of the medical condition and detect any other underlying issue. The Epigenetics test can also help determine the patient’s biological age to estimate the risk of further tissue damage.
Equipped with its own laboratory on the premises, the Renue Center offers advanced Stem Cell Therapy with state-of-the-art technology, specialized medical and scientific staff, and world-class facilities. Visit The Renue Difference to learn more.
Stem Cell Therapy Risks
The risks are low and infrequent because of the therapy’s high safety domain.
The most frequent or possible adverse effects post-SCT can be:
Allergic reactions
Fever
Fatigue or lethargy
Painful injection site
The Hyperbaric Chamber and Stem Cell Therapy
In regenerative medicine, sessions in Hyperbaric Chambers or HBOT (hyperbaric oxygen) can mobilize and vastly increase the number of stem cells in circulation. The HBOT treatment can also increase the concentration of Stem Cells in affected areas and further stimulate the body’s ability to regenerate and repair damaged tissues.
As part of The Renue Difference, the patient receives three Hyperbaric chamber sessions, improving SCT efficacy: one day before the treatment, one on the day of treatment, and one after.
Stem Cell Therapy Outcomes
According to results and clinical outcomes, SCT helps reduce disease progression and speeds up tissue repair.
Equipped with its own laboratory on the premises, The Renue Medical Centre offers advanced Stem Cell Therapy with state-of-the-art technology, specialized medical and scientific staff, and world-class facilities.